光技術情報誌「ライトエッジ」No.3(1995年秋発行)
特集 第7回光源の科学と技術に関する国際会議
(当社発表論文)
誘電体バリア放電を利用したAr,Krエキシマランプの開発
DEVELOPMENT OF Ar,Kr,EXCIMER LAMPS USING DIELECTRIC BARRIR DISCHARGE
技術研究所 応用開発部 技師 菅原寛
はじめに
最近、誘電体バリアを利用した真空紫外(VUV)域の光を放射するエキシマランプが開発されてきたが、これらのいくつかはガスを流しながらの使用条件のため、取り扱いが容易ではなく、工業分野での応用にはあまり適していない[1][2][3][4]。そこで今回、封じきり型のランプ構造からなり、利用し易いヘッドオン型のAr,Krエキシマランプを開発した。
ランプ設計
図1に今回開発したAr,Krエキシマランプの慨略図を示す。電極にはピークtoピーク電圧9kV、周波数20kHzの正弦波電圧が印加される。ランプ入力電力は20Wである。また、封入ガス圧と放電ギャップ長の積は約40kPa・cmである。
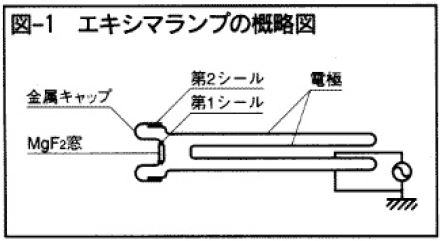
ランプ性能
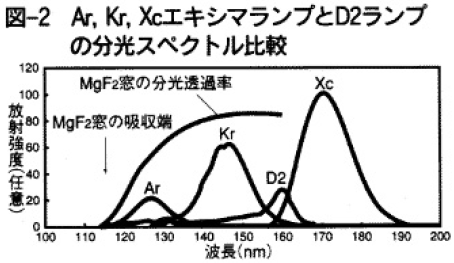
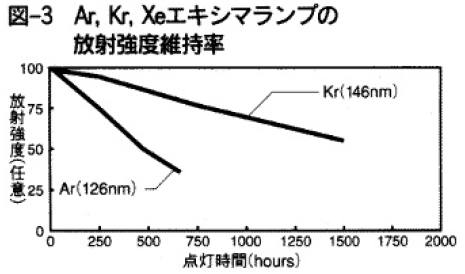
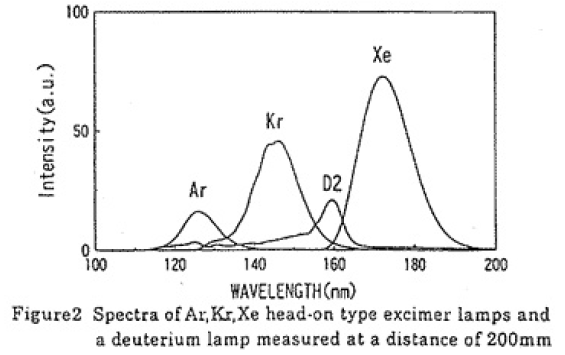
図2にAr,Krエキシマランプと市販のMgF2窓付き30W型の重水素(D2)ランプの分光スペクトルの比較を示す。併せて合成石英ガラス窓のXeのエキシマランプのものも載せている。測定はVUV分光器から200mmの距離で行われた。この結果から、Ar,Krエキシマランプの中心波長はそれぞれ126nm、146nmで、半値幅はそれぞれ10nm、13nmであることがわかる。また、同一波長域でのD2ランプとの出力比はAr,Krそれぞれ4倍、7倍であった。図3にはAr,Krエキシマランプの放射強度の維持率を示す。初期出力の半減時までの点灯時間を寿命と定義すると、Ar,Krエキシマランプの寿命はそれぞれ500時間、1500時間となる。
考察
図3でAr,Krエキシマランプの寿命に大きな差が見られるのは、光取り出し窓、MgF2窓の透過率の劣化スピードの差によるものと考えられる。Krエキシマランプは発光中心波長が146nmで、MgF2窓の初期透過率はこの波長で約80%であるのに対し、Arエキシマランプはそれぞれ126nm、約60%である。このため、Arエキシマランプの方が放射光がより多く窓に吸収され、透過率の劣化スピードを早め、寿命が短くなるものと考えられる。
結論
誘電体バリア放電を利用したへッドオン型のAr,Krエキシマランプを開発した。出力(D2ランプ比)はAr,Krエキシマランプそれぞれ4倍、7倍、また寿命はそれぞれ500時間、1000時間以上である。これらのランプは封じきり構造からなり、取り扱いが容易である。そこで研究室だけでなく、様々な応用に対して多くの工業分野でも利用することができる。
DEVELOPMENT OF Ar,Kr,EXCIMER LAMPS USING DIELECTRIC BARRIR DISCHARGE
H.Sugahara,Y.Ohnishi,H.Matsuno,T.Igarashi ,T.Hiramoto
USHIO INC.,ll94 Sazuchi,Bessho-cho,Himeji-city,Hyogo-pref.,Japan
Introduction
Recentry VUV excimer lamps using dielectric barrier discharge(silent discharge)have been developed[1]. These VUV excimer sources are used for surface cleaning,surface modification,photochemical processes and so on[2][3][4].But these lamps are not easy to handling because of those gas flow structure.Then we deve1oped Ar,Kr head-on type excmer lamps using dielectric barrier discharge.These consist of a sealed-off structure and it is easy to use.
Design
Figure 1 shows a schematic structure of the excimer lamp.This lamp consists of a double-walled coaxial quartz tube and have an MgF2 window on one side of the tube.The electrodes made from metal foil are set up on the outer surface of the outside wall and on the inner surface of the inside wall respectively.An annular part is the discharge space. Sinusoidal voltages are applied between the two electrodes with the frequency of about 20kHz.Pure Ar or Kr gas is enclosed in it for 126nm or 146nm radiation respectively.The MgF2 window is attached to the central part of an annular metal cap made from a nikel plate with frit,and the metal cap is indium-metalizingly attached to the quartz g1ass.The lamp is operated inside a lamp jacket cooled with water in order to protect the sealing part and to prevent the window degradation.A product pd of a gas filling pressure p and a discharge gap length d for both Ar and Kr excimer lamps is about 40kPa・cm.An input power is 20W.
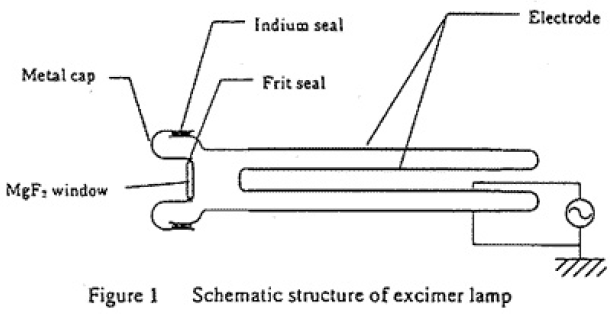
Performance
Figure 2 shows spectra of Ar,Kr,Xe and 30 W-type deuterium(D2)lamp.These are measured on 20W input power for the excimer lamps.Relative radiative intensities were measured with a VUV spectrometer at a place of 200mm apart from the lamp surfaces.Peak wavelength for Ar and Kr excimer spectra are respectively 126nm,146nm and FWHM are respectively 10nm,13nm. The spectra of Ar and Kr excimer lamps are so intensive as high as 4 and 7 times respectively compared with that of the D2 lamp in the same spectral region. Radiative intensity was measured with a fluorescence detector with sodium salicylate.The sensitivity of this detector has been calibrated using a D2 lamp calibrated in Prof. Nakagawa’s laboratory of Saitama University.
The intensities of the Ar and Kr excimer radiation are 2 and 5mW/cm2 at a head of the lamps respectively.Life of the Ar and Kr excimer lamps are respectiveiy 500 and 700 hours provided that the lamp life is defined as the operating time untill reducing by half of the initial radiation output.
Conclusion
We have developed Ar,Kr head-on type excimer lamps using dielectric barrier discharge that can be used in not only laboratories but also in industrial fields.



